Directional Woven Fibers
Woven Fabric materials are used in the wet-wrapping process.
- Materials can be E-glass, S-glass, carbon fiber, woven or stitched together to form strong fabric.
- For oilfield applications, we use directional fiber that is 50/50 or 90/10 and 3-D weave.
- Weight ranges from 1 oz./yard to 600 oz./yard depending on the needs.
Common weave patterns used in oil and gas applications
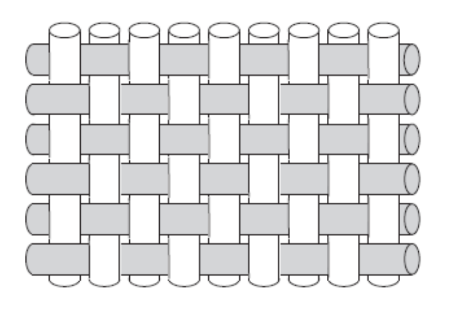
Plain Weave
- Fiber is interlaced in an alternating pattern
- Has good fabric stability
- Most common fabric used in electronics and coating industries
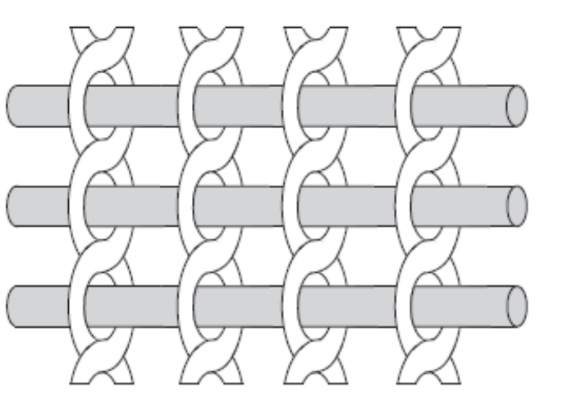
Leno
- Used where relatively low aerial weights but specific thickness needs to be the same
- This fabric is commonly seen in EIFS applications and to set bond line thicknesses for adhesives
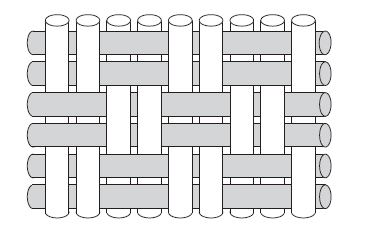
Basket Weave
- Similar to plain weave except that two or more fibers are alternately interlaced over and under one another
- More pliable, flatter and stronger than plain weave, just not as stable
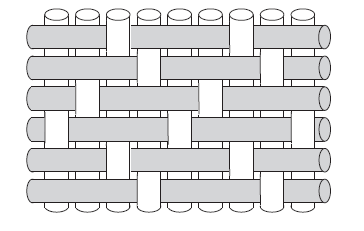
4H Satin
- Relies on three by one interlacing pattern
- The fiber floats over three warp fibers and under one
- Better at conforming to curved surfaces plus more pliable than plain weave
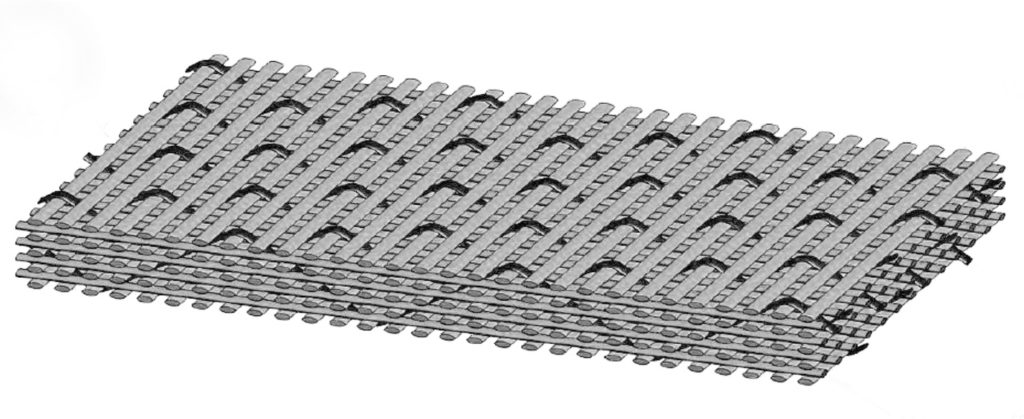
3D Woven Fabric
- 3D woven fabric is 3-Dimension fabric
- Fiberglass makes up the 3D woven fabric that adds strength, which is similar to steel, but is not high in weight
- Compared to a 2D fabric it has limited delamination due to the 3D weave
- The 3D woven fabric has a shorter process time
